Introduction to Money
Money, a concept as old as civilization itself, remains a central pillar in our daily lives, influencing everything from personal choices to global economies. In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the multifarious aspects of money, exploring its various forms, the psychological impacts it has on individuals, and its significant role in different cultures. Our journey will take us through practical discussions on earning, saving, investing, and managing money, as well as examining the ethical considerations and the evolving future landscape of finance. Through this exploration, we aim to provide a deeper understanding of money and its profound influence on our world, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions in an ever-changing economic environment.
Table of Contents
Types of Money
In the realm of finance, “money” serves as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. Over time, the concept of money has evolved, leading to the development of various types that cater to different needs and economic systems. Understanding these types is crucial for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of financial matters.
Fiat Money
Fiat money is the most common type of money in today’s world. It is government-issued currency that isn’t backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver. Instead, its value comes from the trust and confidence that people have in the government that issues it. Examples include the US dollar, the Euro, and the Japanese Yen. Fiat money is typically used for all forms of daily transactions and is the standard in most economies.
The image below shows various fiat currencies from around the world:

Commodity Money
Commodity money, on the other hand, derives its value from the material it’s made of. Historically, commodities like gold, silver, and even shells have been used as money because of their intrinsic value. While not as prevalent in modern times, gold and silver coins are still collected and can be used as a hedge against inflation or economic uncertainty.
Images below are illustrating historical examples of commodity money, such as gold coins:

Digital Currencies
The newest form of money is digital currency, which includes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital assets operate independently of a central authority and use cryptography for security. They are gaining popularity due to their decentralized nature and potential for high returns, although they also come with higher risks and volatility.
See digital e-wallet interface below:
Understanding the different types of money is essential in today’s financial landscape. Each type, from fiat to digital currencies, has its own set of characteristics, uses, and implications. By grasping these concepts, individuals can make more informed decisions about how they handle and interact with money in various forms.
The Psychology of Money
The psychology of money is a fascinating area that explores how our feelings, patterns of thought, and behaviors are influenced by money. Understanding this psychological relationship with money is vital for making informed financial decisions and for overall well-being.
Money and Decision Making
Our relationship with money significantly impacts our decision-making processes. Studies have shown that financial incentives can affect choices in various life aspects, from career paths to personal relationships. The way individuals earn, spend, save, or invest money often reflects their values, goals, and fears.
An illustrative image below depicting decision-making scenarios influenced by money, like shopping:

Emotional Impact of Money
Money is not just a transactional tool; it also has a deep emotional impact. It can be a source of stress, happiness, security, or anxiety. People’s emotional responses to money can shape their financial habits. For example, the fear of loss can lead to risk-averse investment strategies, while optimism might encourage more aggressive financial moves.
Money and Happiness
One of the most debated topics in the psychology of money is its relationship with happiness. While a certain level of financial security is necessary for happiness, studies suggest that beyond a certain point, additional wealth does not significantly increase happiness levels. This concept challenges the common assumption that more money equates to more happiness.
An image below depicts the happiness plateau in relation to income levels:

The Influence of Background and Culture
An individual’s background and cultural influences play a significant role in their attitude towards money. Factors like upbringing, education, and societal norms can shape one’s financial beliefs and behaviors. Understanding these influences can lead to more self-awareness and better financial decisions.
The psychology of money encompasses a wide range of emotions and behaviors. By understanding these psychological aspects, individuals can develop a healthier relationship with money, leading to better financial and personal outcomes.
Earning Money
Earning money is a fundamental aspect of financial life. Whether through employment, entrepreneurship, or investments, the ways in which people earn money are as varied as they are complex. Understanding these avenues can help you choose the best path for your financial goals and lifestyle.
Employment
For most people, earning money primarily comes from employment. This includes salaries, wages, bonuses, and benefits received from working for an employer. Employment can offer stability and predictability in income, as well as potential career growth and skill development opportunities.
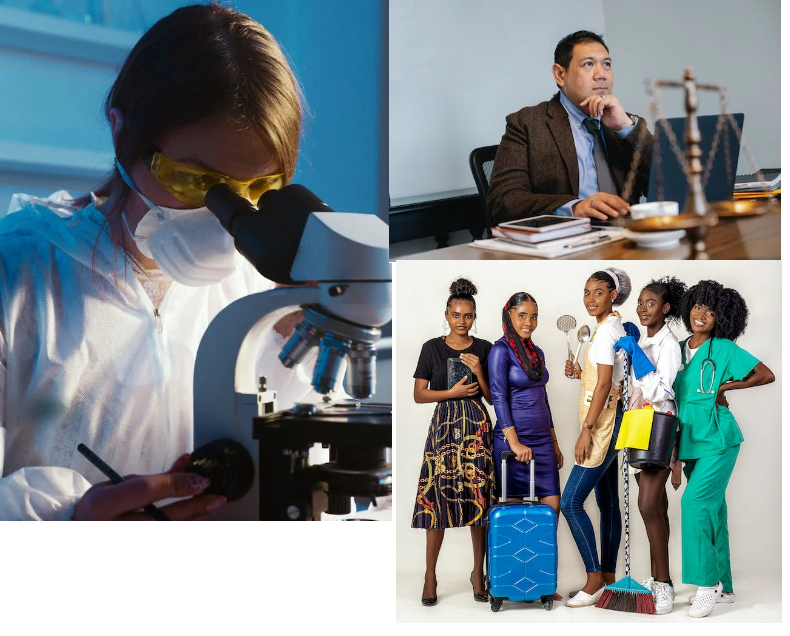
An image below is depicting various professions and visually represent the diversity in employment:

Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is another avenue for earning money, involving starting and running a business. This path can be riskier but offers the potential for higher rewards and greater flexibility. Entrepreneurs often experience a deep sense of satisfaction from creating something successful.
See an idea conception to establishment image below ( image source):

Passive Income
Passive income is money earned with minimal activity, such as dividends from investments, rental income, or earnings from online ventures. This form of earning money is particularly attractive as it can provide financial security and freedom, allowing individuals to earn money even when they are not actively working.
The infographic below explains dividends passive income ( image source):

Investments
Investing money in stocks, bonds, real estate, or other ventures can also be a way to earn money. While it involves risk, smart investments can provide substantial returns. The key is to understand the market, diversify investments, and think long-term.
There are numerous ways to earn money, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Whether you’re employed, running your own business, earning passive income, or investing, understanding these options is crucial for financial growth and stability.
Saving and Investing Money
Saving and investing money are two critical components of financial health and security. While they are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes in personal finance. Understanding the distinction and importance of both can significantly impact your financial future.
Saving Money
Saving money typically involves putting away funds in secure and accessible forms like savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or money market accounts. The primary goal of saving is to preserve capital and have it readily available for emergencies or short-term goals. Savings usually offer lower returns but come with minimal risk and provide a financial safety net.
An image below depicts various savings method like piggy banks etc:

The Importance of an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a crucial part of saving money. It’s a dedicated account where you store a set amount of funds, usually enough to cover three to six months of living expenses. This fund acts as a buffer against unforeseen financial shocks like job loss or medical emergencies.
Investing Money
Investing money, in contrast, is about using your funds to purchase assets that you expect to increase in value over time. Common investment vehicles include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. The aim of investing is to build wealth over the long term, taking advantage of compounding returns. However, it comes with higher risks compared to saving.
An infographic explaining basic investment concepts like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds would be informative.
Balancing Risk and Reward
Understanding and managing risk is key to successful investing. Different investment options come with varying levels of risk and potential returns. Generally, higher risk investments have the potential for higher returns. Diversifying your investments can help mitigate risks and stabilize potential returns.
Both saving and investing money are essential for achieving financial stability and growth. Saving provides a safety net for immediate needs, while investing can help you achieve long-term financial goals. Knowing how to balance and leverage both can lead to a secure and prosperous financial future.
A side-by-side comparison graphic of saving versus investing below highlight their differences and benefits:

Money Management
Money management is a crucial skill that involves budgeting, spending, saving, and investing. Effective money management helps you maximize your financial resources, achieve your financial goals, and secure your financial future.
Budgeting
The cornerstone of good money management is budgeting. It involves tracking your income and expenses to understand where your money is going. This helps in making informed decisions about how to allocate your funds effectively, ensuring that your spending aligns with your financial goals.
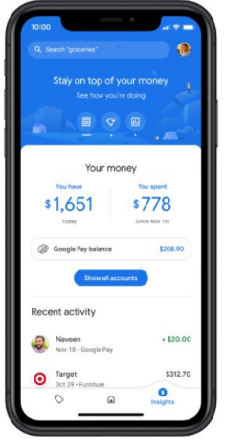
See an image of a sample budget dashboard donuts chart for a particular month illustration below:
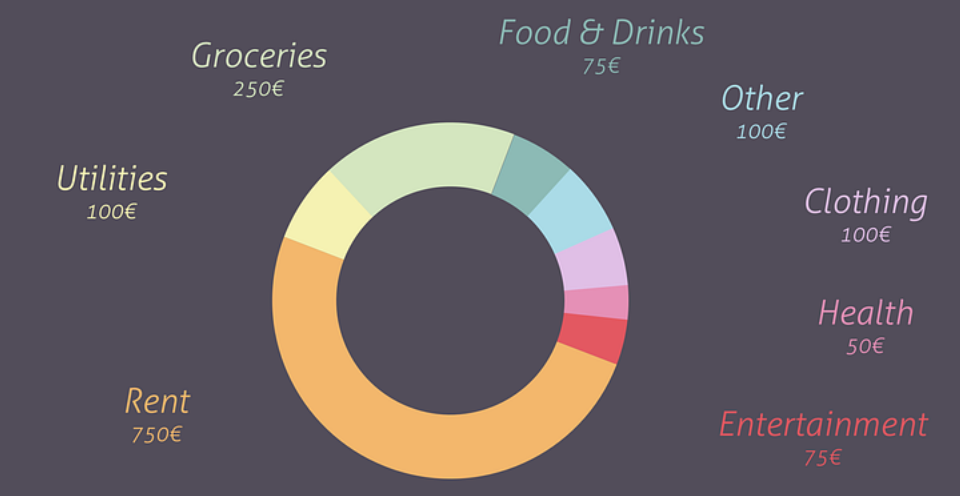
Smart Spending
Smart spending is about making thoughtful and informed choices when it comes to purchasing goods and services. It’s not just about cutting expenses but spending money in a way that adds value to your life. This includes comparing prices, avoiding impulsive buys, and prioritizing spending on needs over wants.
Saving Strategies
Effective money management also involves developing a habit of regular saving. Setting aside a portion of your income for emergencies, future purchases, or investment is essential. Automating your savings can ensure consistency and help in building a substantial fund over time.
Using Financial Tools
There are numerous financial tools and apps available that can simplify the process of money management. These tools can help you track expenses, set budgeting goals, monitor investments, and plan for the future. Utilizing these tools can make managing your finances more efficient and less time-consuming.
Reviewing and Adjusting Your Financial Plan
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your financial plan is an important part of money management. As your financial situation and goals change, so should your approach to managing your money. This ensures that you are always on track to meet your financial objectives.
Effective money management is key to financial stability and success. It involves a combination of budgeting, smart spending, regular saving, and using the right tools to keep track of your finances. By mastering these skills, you can take control of your money and achieve your financial goals.
Use of right tool to keep track of finances is vital in Money Management:

Credit and Loans
redit and loans are integral components of modern financial systems, offering individuals and businesses the opportunity to access funds for various purposes. Understanding how they work is crucial for effective money management and making sound financial decisions.
Understanding Credit
Credit refers to the ability to borrow money with the promise to repay it in the future, typically with interest. It is often accessed through credit cards, lines of credit, or loans. A person’s creditworthiness, commonly measured by their credit score, determines their ability to borrow and the terms of the credit.
Types of Loans
Loans are sums of money borrowed that must be repaid with interest. They come in various forms, including personal loans, mortgages, auto loans, and student loans. Each type of loan is designed for specific purposes and comes with its own set of terms and conditions.
Interest Rates and Terms
The cost of borrowing money is largely determined by interest rates and loan terms. Interest rates can be fixed or variable and are influenced by factors like the borrower’s credit score, loan amount, and economic conditions. Understanding these terms is vital for calculating the total cost of a loan and for choosing the right loan product.
The Importance of Responsible Borrowing
Responsible borrowing involves understanding your capacity to repay a loan and the implications of taking on debt. It’s important to borrow only what you need and have a clear plan for repayment. Mismanaging loans can lead to debt accumulation and adverse impacts on your credit score and financial health.
Building a Good Credit History
Building and maintaining a good credit history is essential for accessing favorable loan terms. This involves timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and regularly checking credit reports for errors. A strong credit history can lead to better loan conditions and lower interest rates in the future.
Credit and loans are powerful financial tools that, when used wisely, can help in achieving various financial goals. However, they require careful consideration and responsible use to ensure they benefit rather than burden your financial situation.
Global Economy and Money
The global economy represents the interconnectedness of national economies across the world, and money plays a central role in this vast network. Understanding how money impacts the global economy can provide valuable insights into international finance, trade, and economic policy.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates are a fundamental aspect of the global economy. These rates determine the value of one country’s currency in terms of another’s and affect international trade, investment, and economic stability. Fluctuations in exchange rates can have significant impacts on a country’s economic performance.
An image below is showing a currency exchange rate board:
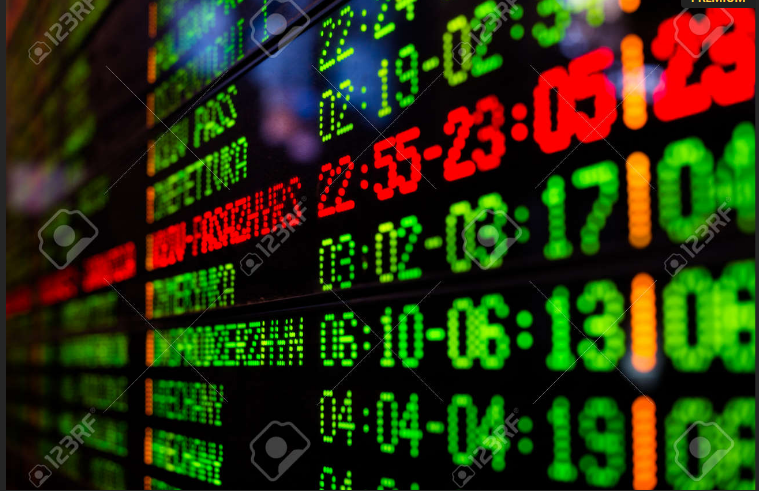

Money and International Trade
Money is the lifeblood of international trade. It enables countries to buy and sell goods and services across borders. The balance of trade, which is the difference between a country’s exports and imports, is a key indicator of economic health. A trade surplus can lead to a stronger currency, while a trade deficit can weaken it.
Impact of Inflation
Inflation, the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, is a critical aspect of how money affects the global economy. Central banks around the world monitor inflation and adjust monetary policy accordingly to maintain economic stability.
Global Financial Markets
The global financial markets, including stock exchanges, bond markets, and commodity markets, play a crucial role in the global economy. These markets facilitate the flow of money and investments globally and are indicators of economic trends and investor sentiment.
Remittances and Global Money Transfers
Remittances, money sent by individuals working abroad to their home countries, are a significant part of the global economy. They are a vital source of income for many countries and can have a profound impact on poverty reduction and economic growth.
See a map below showing major remittance flows from China 2017 worldwide to illustrate the scale and impact of these transfers:
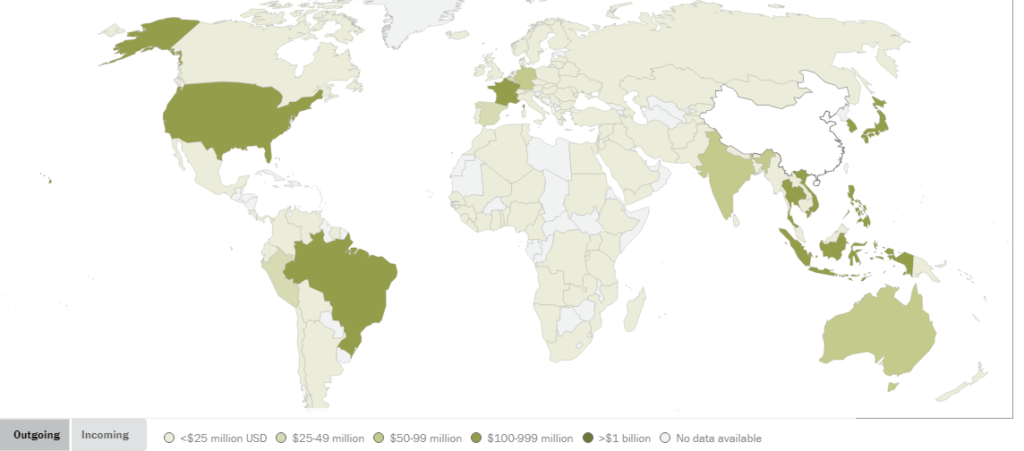
Money’s role in the global economy is multifaceted and complex. From affecting trade and investment to influencing inflation and economic policies, understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping the bigger picture of global economics.
Digital Money and Cryptocurrency
In the evolving landscape of finance, digital money and cryptocurrency have emerged as revolutionary concepts, reshaping how we think about and use money. Understanding these digital forms of currency is essential in the age of technological advancement.
What is Digital Money?
Digital money refers to any means of payment that exists purely in electronic form. Unlike physical money, such as paper currency or coins, digital money is intangible and transferred electronically. This includes transactions made via online banking, electronic transfers, and digital wallets.
See an image below illustrating digital money in a form of online transactions:

Introduction to Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a subset of digital money that uses cryptography for secure transactions. It operates on a technology called blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. The most well-known cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin and Ethereum, but there are thousands of others, each with unique features and uses.
See a visual representation of a blockchain below:
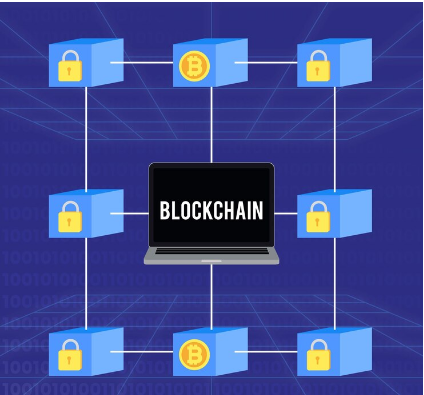
Benefits of Digital Money and Cryptocurrency
Digital money offers convenience, speed, and accessibility, making financial transactions easier and more efficient. Cryptocurrencies go a step further by offering a level of security and anonymity that traditional digital money cannot. They also open possibilities for new financial systems that are more inclusive and less reliant on traditional banking infrastructures.
Risks and Challenges
Despite the benefits, digital money and cryptocurrencies come with risks. Digital transactions are susceptible to cyber threats, and cryptocurrencies are known for their high volatility. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still evolving, posing challenges for users and investors.
The Future of Money
As technology continues to advance, the role of digital money and cryptocurrencies in the global economy is likely to grow. They represent the next step in the evolution of money, offering innovative solutions to traditional financial problems and catering to the digital-first generation.
In conclusion, digital money and cryptocurrency are reshaping the concept of money in the digital age. With their unique benefits and challenges, they are poised to play a significant role in the future of finance.
Money in Different Cultures
Money, while a universal concept, holds different meanings and is used in various ways across cultures. Understanding these cultural nuances of money can provide a broader perspective on its role in society and human interactions.
Cultural Attitudes towards Money
Different cultures have unique attitudes towards earning, saving, spending, and sharing money. For instance, in some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on saving and frugality, while others may place more value on spending and enjoying money. These attitudes are often shaped by historical, economic, and social factors.
Money and Social Norms
In many cultures, money is closely tied to social norms and customs. For example, the practice of giving money as gifts during weddings, festivals, or religious ceremonies varies greatly across cultures. In some societies, discussing money openly is considered taboo, while in others, it’s a routine part of conversation.
Money and Community
The role of money in community relationships is also culturally specific. In some cultures, there’s a strong tradition of community support and pooling resources, while in others, financial independence and self-reliance are more valued. These practices reflect deeper cultural values and community structures.
See the image visuals showcasing community money practices of communal saving circles (Stokvel in South Africa):

Money in Religious and Ethical Contexts
Money’s role in religious and ethical contexts varies significantly across cultures. Many religions have specific teachings about money, such as tithing, almsgiving, or the prohibition of usury. These practices influence how individuals view and use money in their daily lives.
The Impact of Globalization
Globalization has led to a blending of cultural attitudes towards money. Exposure to different economic systems and values has influenced how different cultures perceive and interact with money. This cross-cultural exchange has implications for international business, trade, and finance.
Money in different cultures is a complex and multifaceted subject. The ways in which different societies earn, save, spend, and perceive money are deeply rooted in cultural norms and values. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the diverse roles money plays around the world.
Financial Education and Literacy
Financial education and literacy are essential for navigating today’s complex financial landscapes. They involve understanding and effectively using various financial skills, including personal financial management, budgeting, and investing. The importance of this knowledge cannot be overstated, as it empowers individuals to make informed and effective decisions with their money.
The Basics of Financial Literacy
Financial literacy begins with mastering basic concepts like budgeting, saving, and understanding credit and loans. These foundational skills are crucial for managing day-to-day financial tasks and for planning long-term financial goals.
The Role of Financial Education
Financial education provides the tools and knowledge for understanding money management, investment strategies, and the economic forces that affect personal finances. It’s a lifelong process that can begin as early as childhood and continue through all stages of life. Quality financial education can lead to better financial behaviors and increased financial security.
Managing Debt and Credit
Understanding how to manage debt and maintain good credit is a crucial aspect of financial literacy. It involves knowing how to use credit cards responsibly, how to manage loans, and how to build a good credit history. These skills are essential for major life decisions like buying a home or starting a business.
Investment and Retirement Planning
Another important aspect of financial literacy is understanding how to invest money and plan for retirement. This includes knowledge about different investment options, risk management, and the importance of starting retirement savings early..
Access to Financial Education Resources
Thankfully, there are numerous resources available for those seeking to improve their financial literacy, from online courses and workshops to books and podcasts. Utilizing these resources can significantly enhance one’s ability to make sound financial decisions.
Financial education and literacy are key to achieving financial independence and security. They equip individuals with the necessary tools to navigate the complexities of the financial world and to make informed decisions about their money.

Money and Ethics
The relationship between money and ethics involves a complex interplay of financial practices, moral principles, and societal values. In this context, ethical considerations are paramount in guiding how money is earned, spent, and managed. Understanding these ethical dimensions is crucial for individuals and organizations alike, fostering responsible financial behavior and decision-making.
Ethical Earning
Ethical earning is about acquiring money in ways that are not only legal but also morally sound. This encompasses fair business practices, honest advertising, and the avoidance of exploiting labor or resources. It’s important for businesses and individuals to consider the broader impact of their actions in the pursuit of financial gain.
Ethical Spending
Ethical spending involves being mindful of where and how money is spent. This includes supporting businesses that uphold ethical standards, such as those committed to environmental sustainability, fair labor practices, and ethical sourcing. Consumers increasingly recognize their power to influence societal and environmental issues through their spending choices.
.
Money in Politics
The intersection of money and politics is a critical area of ethical concern. Issues like campaign finance, lobbying, and political donations raise questions about the influence of money on political decisions and policies. Transparency and regulations in political funding are essential to ensure fairness and integrity in the democratic process.

Philanthropy and Charitable Giving
Ethical considerations also extend to how money is used for the greater good. Philanthropy and charitable giving represent ways in which individuals and corporations can contribute positively to society. The ethics of philanthropy involve not just the act of giving but also ensuring that the funds are used effectively and responsibly.
Personal Finance Ethics
On a personal level, ethical money management involves honesty in financial dealings, such as paying taxes and debts. It also includes being financially responsible to oneself and others, like family members or employees, who may be impacted by one’s financial decisions.
The intersection of money and ethics encompasses a wide array of practices and considerations. From the way money is earned and spent to its role in politics and philanthropy, ethical considerations are key to ensuring that financial activities contribute positively to society.
The Future of Money
The future of money is a topic that captivates economists, technologists, and the general public alike. As technology advances, the way we interact with money is rapidly evolving. Understanding these changes is crucial for adapting to the upcoming financial landscape.
Digital Transformation
The digital transformation in finance is leading towards more electronic transactions and less physical cash. Contactless payments, mobile wallets, and online banking are becoming the norm. The future may see a further shift towards entirely digital currencies, reducing the need for physical money.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are at the forefront of changing how we perceive and use money. These technologies offer decentralization, increased security, and potential for creating more inclusive financial systems. While they face regulatory and adoption challenges, their impact on the future of money is expected to be significant.
The Rise of Fintech
Financial technology, or fintech, is revolutionizing money management, lending, investing, and payments. Fintech companies are innovating at a rapid pace, offering solutions that are more user-friendly, efficient, and accessible than traditional financial services. This trend is likely to continue, reshaping the financial services industry.
See below image showcasing fintech app:
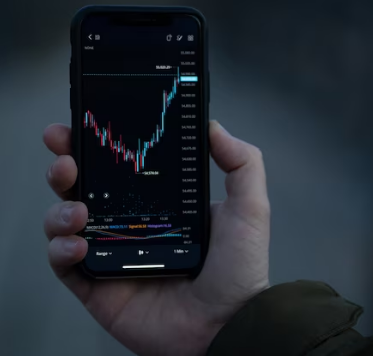
Global Implications
The evolution of money has significant global implications, especially in terms of financial inclusion. Digital money can provide access to financial services for the unbanked or underbanked populations. However, it also raises concerns about privacy, security, and the digital divide between different regions of the world.
Sustainability and Ethics
As we move towards the future of money, issues of sustainability and ethics gain prominence. There is an increasing call for financial systems and practices that are not only efficient but also environmentally sustainable and ethically sound.
The future of money is poised to be more digital, decentralized, and innovative. While this brings numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges that need to be navigated carefully. Staying informed and adaptable is key to thriving in this evolving financial landscape.
Conclusion
In exploring the multifaceted world of money through various lenses – from its types and psychology to its role in different cultures and the future financial landscape – we gain a comprehensive understanding of its profound impact on our lives. Whether discussing practical aspects like earning, saving, investing, and managing money, or delving into the more complex realms of credit, loans, and the ethical implications of financial decisions, it’s clear that money is a pivotal force in both personal and global contexts.
As we conclude this journey through the world of money, remember that the key to successful financial management lies in continuous learning, adaptability, and making informed decisions. Whether you’re navigating day-to-day budgeting, planning for your retirement, or making investment choices, the principles and insights shared in this blog can serve as a guide.
Money, in all its forms and functions, is more than just a means of transaction. It’s a tool that, when understood and used wisely, can help achieve financial stability, security, and even prosperity. As we look towards the future, staying informed and adaptable in the face of changing financial landscapes will be crucial in harnessing the full potential of money in enhancing our lives.
Remember, the journey to financial wisdom is ongoing, and each step, whether small or significant, is a move towards a more secure and financially savvy future. Keep exploring, learning, and growing in your financial journey.



